
The digital age has ushered in a new era of automation and intelligence, with Artificial Intelligence (AI) emerging as a transformative force across industries. The unrelenting march of AI has irrevocably altered the landscape across industries. AI holds immense potential for the public sector, promising efficiency gains, improved decision-making, automating repetitive tasks, generating personalized recommendations, and enhanced citizen services. While AI significantly benefits citizens and government agencies, it presents unique challenges requiring careful consideration when implementing AI solutions. Here is a closer look at the opportunities and challenges of AI transformation in the public sector and specific strategies to address these challenges.
Embedding AI in the Public Sector: A Catalyst for Transformation
The public sector stands on the precipice of a revolution driven by AI. AI offers many opportunities to enhance efficiency, improve citizen services, and empower the government to tackle complex challenges. Below are a few ways AI is poised to transform the public sphere.
Boosting Efficiency and Productivity: AI can automate and streamline repetitive tasks such as data entry, form processing, etc., currently handled by employees, allowing employees to dedicate their expertise to areas requiring human judgment and empathy.
Data-Driven Decision Making: AI's ability to analyze vast amounts of data can revolutionize how governments make decisions. By providing data-driven insights, AI can empower policymakers to make informed decisions that address citizens’ needs more effectively.
Personalized Citizen Services: AI can tailor experiences to individual needs. Government agencies can leverage AI to personalize citizen interactions, providing targeted information and support services.
Innovation in Public Service Delivery: AI opens doors for groundbreaking advancements in public service delivery. For example, law enforcement agencies can leverage AI for crime prediction and prevention, allocating resources more effectively and improving public safety. AI-powered healthcare systems can analyze patient data to predict health risks and personalize treatment plans, ultimately leading to better health outcomes.
By embracing AI and its capabilities, governments can usher in an era of greater efficiency, better decision-making, and a more responsive and citizen-centric public service ecosystem. Overall, AI presents a substantial opportunity for the public sector to improve the citizens’ experience.
Public Sector AI Adoption: A Road Paved with Challenges
The public sector is on the cusp of a significant transformation driven by AI. While AI presents a transformative opportunity for the public sector, its adoption is challenging. Here is a breakdown of a few problematic areas to navigate.
Data Challenges
Data Quality and Accessibility: Public sector data often resides scattered across different departments and agencies in isolated systems. The data in these siloed systems makes it challenging to aggregate clean and high-quality data for AI training. Fragmented data storage hinders the ability to extract meaningful insights for AI models.
Data Privacy, Security, and Bias: Robust data security measures are crucial to ensure responsible AI development and prevent potential breaches or misuse. AI models trained on biased data can perpetuate societal inequalities.
Organizational Challenges
Legacy Systems: Public sector entities often rely on dated IT infrastructure, hindering seamless integration with AI solutions. Modernization efforts might be necessary to create a technology stack that supports AI adoption.
Workforce Skills Gap: Public sector employees may need more skills to develop, manage, and utilize AI effectively. Training programs are crucial to equip government workers with the technical knowledge and understanding required for the AI era.
Cultural Resistance: Public sector cultures may be risk-averse and resistant to change. Effective communication strategies and user-centric design can help overcome this resistance and encourage AI adoption.
Legal and Ethical Challenges
Algorithmic Transparency: Black-box AI models can be challenging to explain, raising concerns about accountability and transparency in decision-making processes. Public trust requires explainable AI (XAI) models that provide insights into how decisions are made.
Algorithmic Bias: As mentioned earlier, biased data can lead to biased AI models that discriminate against certain groups. Mitigating algorithmic bias requires proactive measures throughout the development process to ensure fairness.
Regulation and Oversight: Evolving regulations around AI use in the public sector require careful adherence to ensure responsible development and deployment. Staying updated on rules and ensuring compliance is crucial.
Public Perception and Trust
Privacy Concerns: Citizens might be apprehensive about AI's potential for government surveillance and data misuse. Transparency and clear communication are vital for building trust in AI initiatives.
Job Displacement Fears: Automation through AI can raise concerns about job losses in the public sector. Focus on reskilling and upskilling the existing workforce and creating complementary roles alongside AI can alleviate these fears.
Ethical Considerations: To maintain public trust, ethical questions surrounding the use of AI in areas like facial recognition or predictive policing need to be addressed proactively. Open discussions and clear ethical frameworks are important.
Overcoming AI Challenges in the Public Sector: Strategies for Success
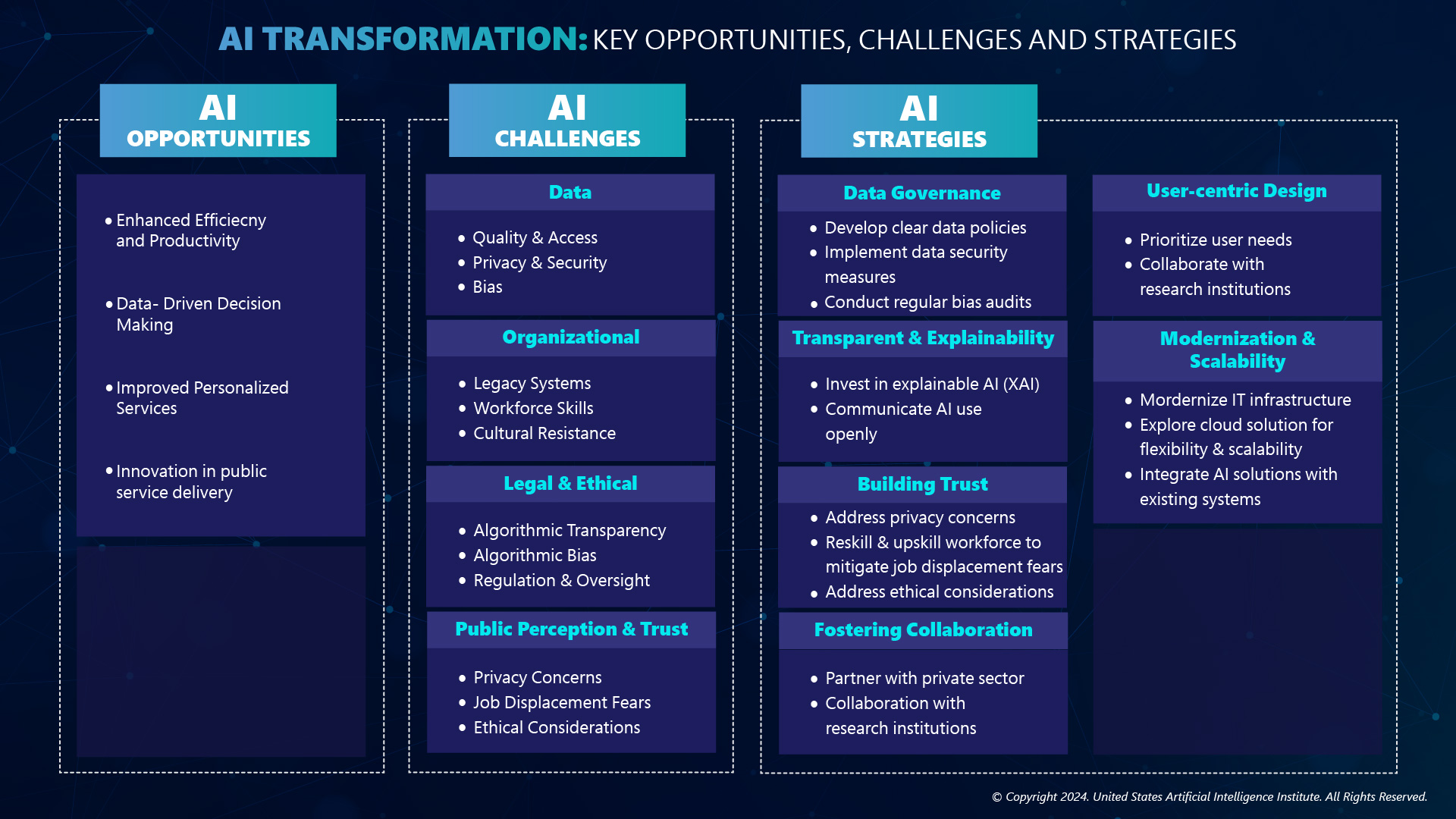
The AI transformation in the public sector is promising. Still, challenges related to embedding AI in the public sector must be identified and addressed for the transformation to be successful. Figure 1 shows some key AI transformation opportunities, challenges, and strategies for addressing these challenges in the public sector.
Develop Robust Data Governance Frameworks: Implement clear policies and procedures regarding data collection, storage, usage, and security. Regularly audit AI systems for potential bias. Establish robust data governance frameworks to ensure data quality, security, and responsible AI development practices.
Data Privacy and Security: Public institutions hold vast amounts of sensitive data. Balancing innovation with data protection regulations is a critical concern. Ensuring robust data security and user privacy is paramount when implementing AI solutions.
Focus on User Needs: Prioritize user-centric design that focuses on improving citizen experiences and public service delivery.
Open Communication and Transparency: Maintain open communication with stakeholders, addressing concerns about privacy, ethics, and job displacement.
Collaboration and Partnerships: Public-private partnerships can leverage private sector expertise and resources to address challenges in data governance and talent acquisition.
Focus on Transparency and Explainability: AI models can be complex black boxes with opaque decision-making processes. Public trust requires transparency in how AI reaches conclusions, especially for decisions impacting citizens’ lives. Invest in XAI techniques that allow users to understand the logic behind AI decisions.
Promote Equity and Fairness: Conduct regular bias audits of AI models and datasets. Develop diverse training data and implement fairness metrics to monitor AI outputs for potential bias.
Invest in Workforce Development: AI automation can potentially displace specific public sector jobs. Upskilling and reskilling the workforce is essential to prepare employees for new roles that complement, rather than replace, human expertise. Provide training opportunities to equip the public sector workforce with the skills to work effectively alongside AI.
Modernize Legacy Systems: Many public institutions need to work on updating infrastructure and legacy systems. Integrating AI solutions with legacy systems can be complex and expensive. Gradually modernize legacy infrastructure. Integrate AI solutions with existing systems. Explore innovative solutions for greater flexibility and scalability.
Engage with the Public: Public trust is paramount for successful AI implementation. Citizens might be apprehensive about government surveillance and data misuse. Communicate the benefits and potential risks of AI adoption clearly and openly. Address public concerns and create opportunities for public feedback throughout the AI transformation process.
Collaboration and Partnerships: Public-private partnerships can leverage private sector expertise and resources to address challenges like data access and talent acquisition, addressing concerns about privacy, ethics, and job protection.
Equity and Fairness: Careful data curation and algorithmic fairness assessments are essential to mitigate data bias and ensure fair outcomes for all citizens. Mitigating bias in data, AI development, and deployment is crucial.
Public Perception: Concerns about job displacement, algorithmic bias, and government overreach can create public resistance to AI adoption. Fostering trust and transparency is critical for successful public acceptance.
Regulatory Landscape: AI regulations are still evolving and creating uncertainty for public agencies implementing AI solutions. Compliance with the regulatory requirements is crucial. Ensuring compliance with existing and emerging regulations can be complex.
Conclusions
AI is a powerful transformation tool that presents unique challenges and opportunities. Government organizations can take proactive steps to thrive in the ever-evolving AI era. Well-defined strategies can help overcome challenges and harness AI’s potential in the public sector. In the above figure lists the vital opportunities, challenges, and strategies to consider during AI transformation. Building trust is critical in successful AI transformation, which requires focusing on XAI solutions that allow human oversight and prioritizing data governance with robust frameworks for data privacy, security, and responsible collection practices.
Additionally, concerns around job displacement due to AI can be addressed by focusing on reskilling and upskilling the existing workforce while creating complementary roles alongside AI. Engaging with the public openly about AI benefits and risks while addressing concerns and creating opportunities for feedback is crucial throughout the AI transformation process. Finally, fostering collaboration with private sector companies and research institutions can accelerate AI adoption. The public sector can embed AI for a better future by implementing effective strategies.
Follow us: