
Artificial Intelligence is an interdisciplinary field combining mathematics, computer science, electronics, and statistics to convert traditional bit sequences ('0' or '1') to mimic natural human brain cognition. As of 2025, achievements in the field of AI are still far from mimicking human-level cognition. On the contrary, the human brain has limitations on how much it can process in terms of cognitive functions. For example, humans cannot read 1000 pages of text in one hour or perform a multiplication of two 20-digit numbers within a fraction of a second. To oversimplify the AI endeavor, sensors receive data, which is then converted into insights, features, or literacy. Depending on the data, these features are processed through complex, multi-dimensional algorithms (aka Neural Networks) that can scientifically detect changes and patterns at a scale of computing beyond the capability of the human brain and traditional computing infrastructure.
The Journey
Artificial Intelligence research and development is on its way to surpass human cognitive-level intelligence. The spirit of the research is pursued in multiple areas, each focused on specialized domains within the field of Artificial Intelligence.
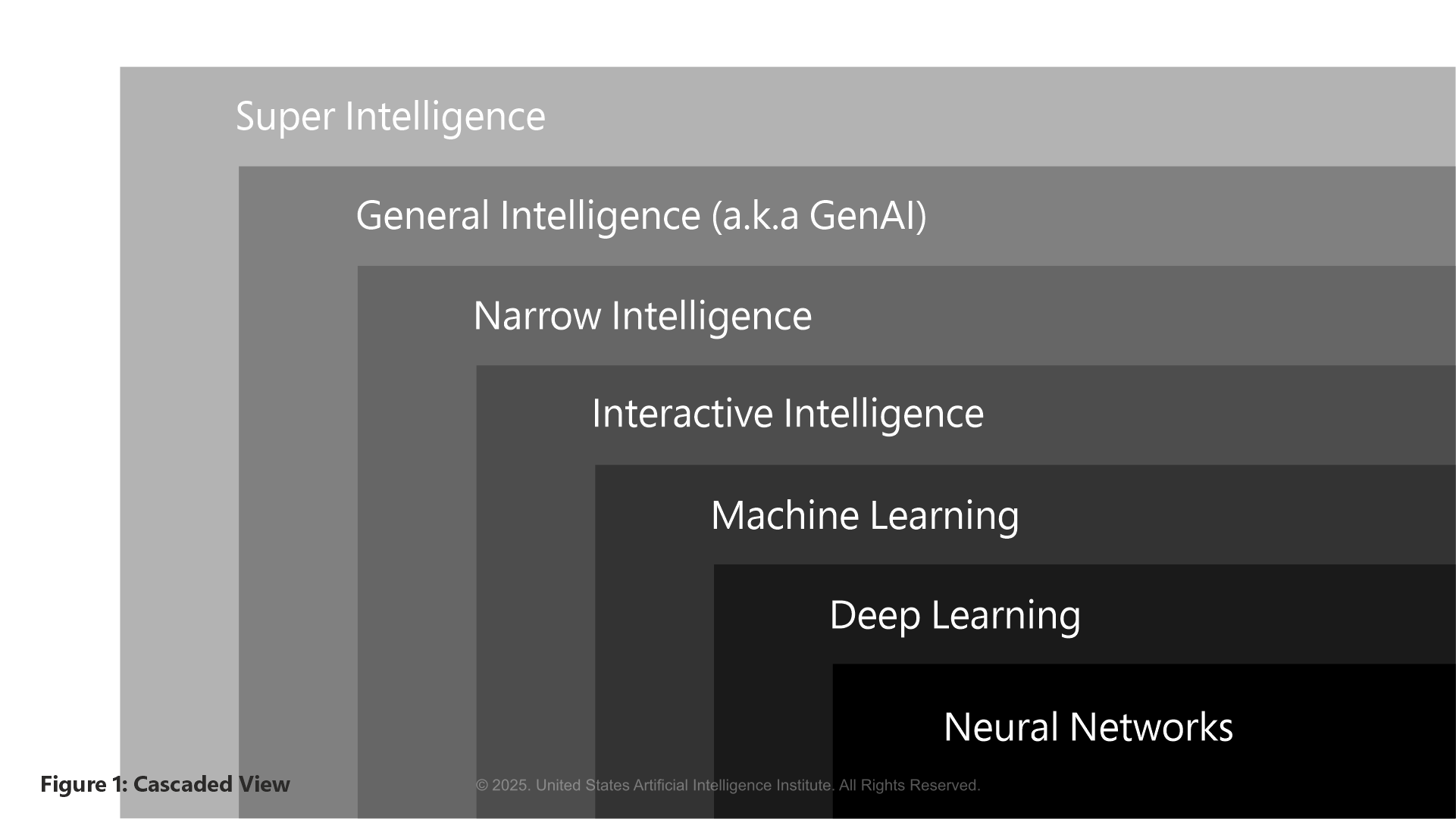
Figure 1 is an effort to portray the cascade view of AI domain research. Let us take a bottom-to-top approach. Neural Networks are a type of machine learning model that processes the data using nodes and layers arrangement to predict an output value. Deep Learning is an Artificial Neural Network with multiple layers, primarily used to detect images, audio inputs, and NLP capability. Machine Learning is a proven and robust technique that enables computing infrastructure to autonomously learn from data using trained statistical models, without the need for explicit programming to learn. Interactive Intelligence is a combination of AI and human interactions, where the AI system learns, adapts, and improves based on the interactions and feedback provided by humans. The Narrow Intelligence performs a single task for which it is specifically trained, operates within a predefined range of functions for a particular use case, typically used for automating complex business processes. Artificial General Intelligence is human-like intelligence capabilities encompassing creativity, innovation, general problem-solving, and reasoning abilities. Artificial Superintelligence surpasses human capabilities and has the potential to solve planetary-level problems. However, this type of intelligence could also pose a threat.
Data Literacy
Data literacy is the ability to read, understand, create, and communicate data as information. The human brain can effortlessly perceive the world around us and generate contextual data insights on the fly. The figure below is an attempt to visualize the perception of the world around us in an “Artificial Setting” and a “Natural Setting.”
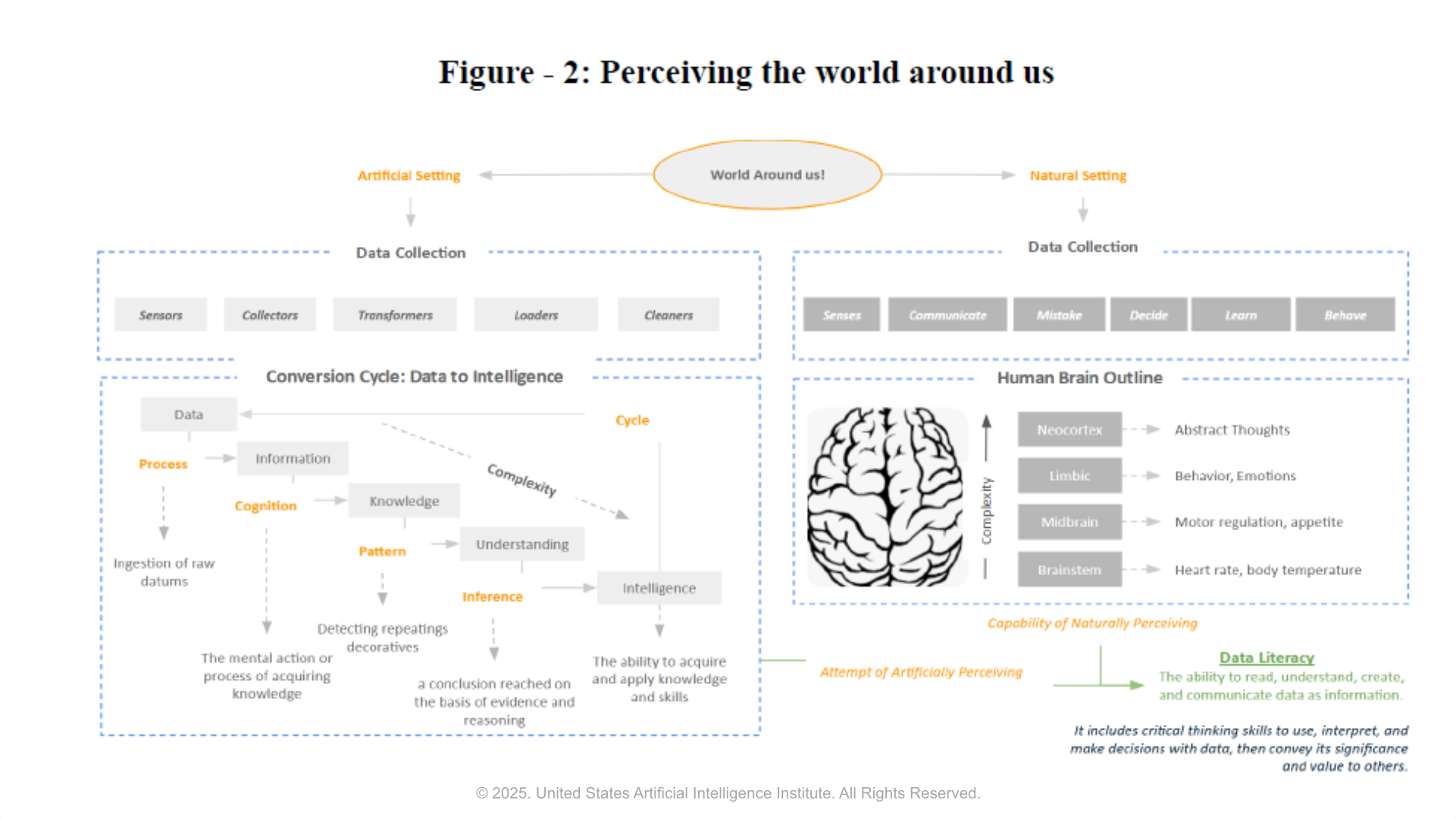
In an Artificial Setting, for a computing infrastructure to mimic a cognitive function, it must be provided with literacy-enabled data, and it can be accomplished by data collection and to intelligence conversion process. On the other hand, for a human to perform a multi-magnitude cognitive function, it will be done naturally without a power supply, computing infrastructure, or any special algorithms if the senses and training required to perform the cognitive function within a context are not impaired. Here is a simple example: In a flower garden, for a camera to detect a 'rose' flower, it must be equipped with a complex AI solution. In contrast, humans can identify a rose flower with a single glance at the garden.
The goal of literacy-enabled data is to create models that are consumed by unsupervised, semi-supervised, supervised, and reinforcement learning methods. Within a given context, the effectiveness of a model directly depends on the data on which it is trained. These models aid an Artificial Intelligence system in making predictions, recognizing patterns, or automating processes. At a minimum, a model typically has training, validation, and testing datasets.
System View
An artificial intelligence system consists of five logical subsystems. The first subsystem, the Cognitive Subsystem, focuses on cognitive capabilities such as predicting, decision-making, object/event detection, reasoning, natural language processing (NLP), and reinforcement learning. The Cognitive Subsystem offers loosely coupled logic blocks that can be reused for various cognitive functions. The second subsystem, the Computing Subsystem, houses the computing power, data, and configurations required for the Cognitive Subsystem to operate. The third subsystem, the Interactive Response Subsystem, facilitates a user mechanism to invoke or interact with the capabilities of the overall system. The fourth subsystem, the Data Models, acts as the core, providing quality data for training, validating, and testing the system's overall performance and effectiveness. The final subsystem consists of the toolset or technologies used to build the AI solution. The rule of thumb for AI transformation is to develop these subsystems independently while ensuring they remain interoperable with other systems both within and outside the context of the Artificial Intelligence Agent/System.
Prompt Engineering
A prompt is an interaction with an AI system that consists of an input(request) and optional fine-tuning parameters. Prompt-ready is a state of an AI system indicating its readiness to accept the prompts and respond based on its training dataset. Prompting or Prompt Engineering is an attempt to interact with an AI system using a set of best practices to frame a productive prompt that returns the desired output from the AI System. While interacting with an AI agent, a user can learn useful techniques to achieve the objectives of the prompt. Below are a few frequently used prompting techniques:
Conclusion
The primary objective of this AI transformation article is to present my personal learning experience of AI and identify the critical components of an artificial intelligence system agent. The secondary objective is to provide a foundational understanding of AI transformation skills that can be applied in any business context, enabling the overall AI transformation to benefit from educated and high-quality contributions. The article provides a brief overview of the critical components and their role in achieving the overall objectives of the system. It is designed to spark the curiosity of readers, encouraging them to explore further knowledge or enroll in training that may apply to their roles. The selected use case of using AI to investigate a 'rejected' claim is a typical scenario faced by most insurance companies in the industry. The proposed AI transformation plan will turn the investigation of rejected claims into an efficient operating model for these companies. The companies will benefit from the AI transformation by meeting the 24-hour TAT, avoiding significant contractual penalties and synergies from staffing, and improving access to the healthcare experience of claim submitters due to reduced SLAs.
Follow us: